Manuka honey for IBS: A natural remedy to support gut health
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a long-term chronic condition that affects the lower GI tract, namely the small intestine, large intestine and colon.
It can be triggered by a range of causes, including digestive tract infections, an unhealthy balance of gut bacteria, certain types of foods or a problem with the way the gut and brain work together.
Although there is currently no cure for IBS, it is often treated with antibiotics, dietary changes and in some cases medication to relieve symptoms.
But have you ever considered how you can incorporate Manuka honey for IBS management into your diet? Helping to improve and maintain the balance of your gut bacteria, high-strength Manuka honey can also reduce IBS flare ups.
Let’s take a closer look at how our medicinal-grade Manuka honey supports gut health and can help alleviate IBS discomfort.
How high MGO-rated Manuka honey supports a healthy gut
Honey has long been used to promote good digestive health and treat gastrointestinal conditions. Dating back many centuries, Roman physicians would prescribe honey for diarrhea and constipation. It has also been widely used across Europe and Arab countries for hundreds of years.
But not all honeys are equal in their restorative powers. To enjoy the benefits of its natural antibacterial, antibiotic and prebiotic properties, it’s important to choose a high MGO-rated Manuka honey (MGO 1000 - 1900). The higher the MGO number, the higher the bioactivity and the more potent the health benefits for IBS symptoms.
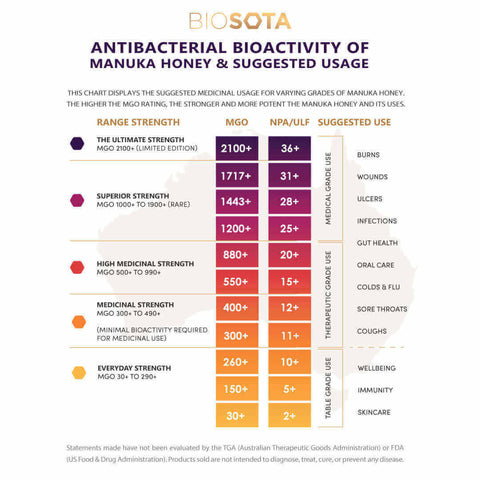
The role of Manuka honey in restoring gut health for post-infectious IBS
In a recent study researchers found that the risk of developing IBS increases six-fold after a gastrointestinal infection.
Other research also indicates that antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and prebiotic honey can reduce infection-causing gut bacteria such as Salmonella, Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Clostridiodes difficile (potentially life-threatening diarrhea). At the same time, it also stimulates the growth of good bacteria.
To help build and maintain a healthy gut environment, taking a regular dose of superior-strength Manuka honey not only aids in the prevention of harmful bacteria, it also helps fight bugs (like those nasty ones that cause food poisoning). This, in turn, can have a positive effect on reducing the risk of post-infectious IBS.
Antibacterial benefits of Manuka honey for IBS
The antibacterial properties of high MGO Manuka honey naturally combat harmful bacteria, especially those that cause gastroenteritis. A regular dose of this healing honey can also potentially reduce the duration and severity of IBS symptoms.
The power of Manuka honey’s prebiotic properties
The prebiotic qualities of Manuka honey make it super effective in strengthening and stimulating good bacteria while reducing the bad ones. This helps to create a healthy, well-balanced gut environment and aids in reducing painful and uncomfortable IBS flare-ups.
Taking Manuka honey to reduce inflammation in the gut
Studies indicate that IBS can cause low-grade intestinal inflammation. Because Manuka honey is packed with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, it can alleviate IBS discomfort by reducing bloating and inflammation in the gut.

Creating a healthier gut environment can help reduce IBS flare-ups
While there is no existing cure for IBS, medicinal-grade Manuka honey is a natural way to support good gut health, which in turn, can help reduce flare-ups and severity of symptoms.
As always, it is important to first consult your healthcare provider, as people with IBS can have varying levels of sensitivity to honey. If you are following the FODMAPS diet, Manuka honey may not be advisable during IBS flareups. It may instead be better to slowly introduce it into your diet once symptoms have disappeared.
References:
- The Potential of Honey as a Prebiotic Food to Re-engineer the Gut Microbiome Toward a Healthy State
- Post-infectious irritable bowel syndrome
- The Potential of Honey as a Prebiotic Food to Re-engineer the Gut Microbiome Toward a Healthy State
- Inflammation in irritable bowel syndrome: Myth or new treatment target


